ヒストンバリアントH2A.Z非ゲノム情報の複製における分子機構と制御クロストーク
研究内容
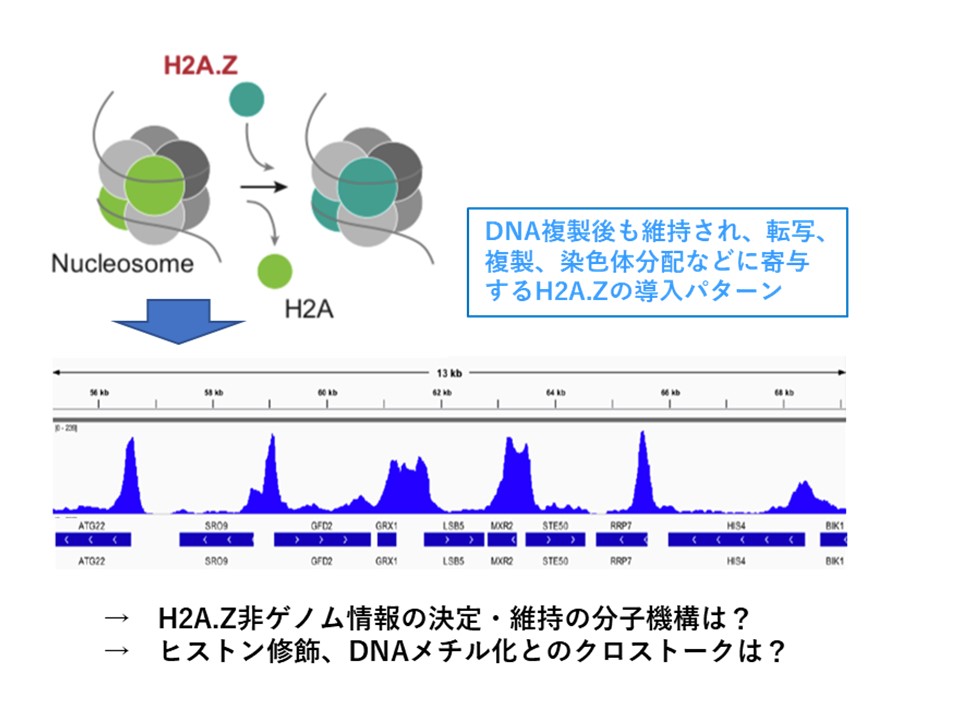
通常のコアヒストンとは配列が部分的に異なるヒストンバリアントの導入が、エピジェネティック制御に重要な役割を果たしています。ヒストンバリアントH2A.Zは、酵母、線虫、植物、脊椎動物細胞まで、進化的に最も普遍的に存在するヒストンバリアントです。H2A.ZはDNA複製終了後にSWR1/SRCAPクロマチンリモデリング複合体によってゲノム上の特定領域のヌクレオソームに導入され、この部位特異的H2A.Z導入が、転写・複製・染色体分配、さらには発生・分化・細胞がん化にも重要な役割を果たしています。H2A.Z導入部位は多くの遺伝子のプロモーターに検出され、その導入の位置情報はDNA複製後も維持されます。しかし、H2A.Zの導入位置を決定する機構、および複製後もH2A.Z導入パターンが維持される機構は不明です。さらに、H2A.ZとH3K4、H3K27、H3K36、H4K20ヒストンメチル化、H2A.ZとDNAメチル化とのクロストークも示唆されていますが、その分子機構については不明です。そこで本研究では、出芽酵母、線虫、脊椎動物細胞などのモデル生物実験系を用いて、①遺伝子プロモーター領域におけるH2A.Z非ゲノム情報が、どのような分子機構で決定・維持されているのか? ②H2A.Zの非ゲノム情報が、他のヒストン修飾情報やDNAメチル化情報の複製・維持にどのように関与するか?を、明らかにすることを目指します。
主な論文
- Arimura, Y., Ikura, M., Fujita, R., Noda, M., Kobayashi, W., Horikoshi, N., Sun, J., Shi, L., Kusakabe, M., Harata, M., Ohkawa, Y., Tashiro, S., Kimura, H., Ikura, T., *Kurumizaka, H. Cancer-associated mutations of histones H2B, H3.1 and H2A.Z.1 affect the structure and stability of the nucleosome. Nucl Acids Res 46, 10007-10018 (2018)
- Kusakabe, M., Oku, H., Matsuda, R., Hori, T., Muto, A., Igarashi, K., Fukagawa, T., *Harata, M. Genetic complementation analysis showed distinct contributions of the N-terminal tail of H2A.Z to epigenetic regulations. Genes Cells 21, 122-135 (2016)
- Horigome, C., Oma, Y., Konishi, T., Schmid, R., Marcomini, I., Hauer, M.H., Dion, V., Harata, M., *Gasser, S.M. SWR1 and INO80 chromatin remodelers contribute to DNA double-strand break perinuclear anchorage site choice. Mol Cell 55, 626-639 (2014)
- Maruyama, E.O., Hori, T., Tanabe, H., Kitamura, H., Matsuda, R., Tone, S., Hozak, P., Habermann, F.A., von Hase, J., Cremer, C., Fukagawa, T., *Harata, M. The actin family member Arp6 and the histone variant H2A.Z are required for spatial positioning of chromatin in chicken cell nuclei. J Cell Sci 125, 3739-3743 (2012)
- Yoshida, T, Shimada, K., Oma, Y., Kalck, V., Akimura, K., Taddei, A., Iwahashi, H., Kugou, K., Ohta, K., Gasser, S.M., *Harata, M. Actin-related protein Arp6 influences H2AZ-dependent and -independent gene expression and links ribosomal protein genes to nuclear pores. PLoS Genet 6, e1000910 (2010)
 原田 昌彦
原田 昌彦