エピゲノムリプログラミングのゆらぎが生殖細胞分化に与える影響の理解
研究内容
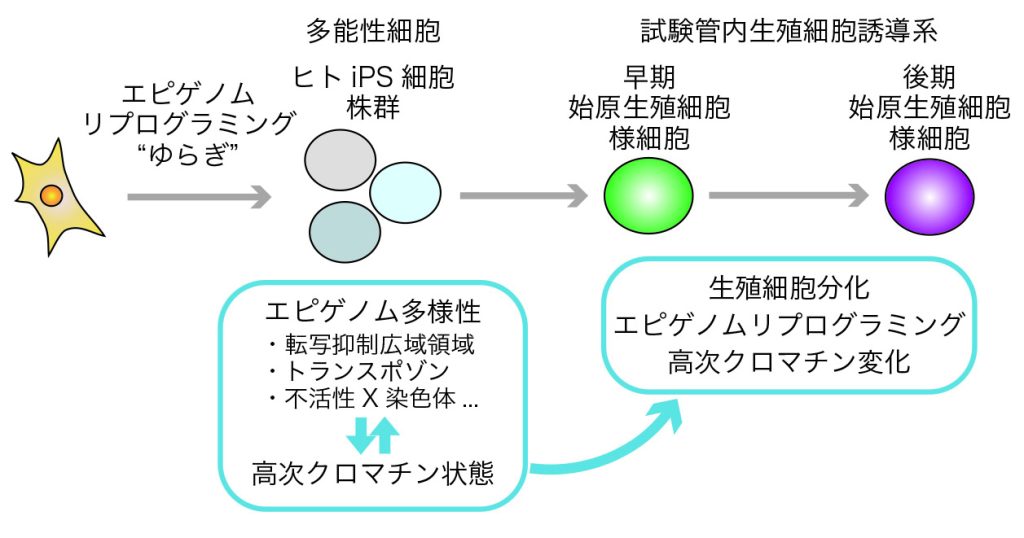
エピゲノムリプログラミングは、エピゲノム状態のゲノムワイドな変化を介して細胞の運命変化や初期化を促す生命現象であり、哺乳類の初期胚や生殖細胞の発生、さらにiPS細胞(人工多能性幹細胞)の樹立に重要な役割を果たす現象です。近年のクロマチン研究から、エピゲノム状態の維持および変化は、クロマチンの高次構造や核内動態と連動しながら協調的に制御されていることが示唆されています。しかし、リプログラミング過程で起きるゲノムワイドなエピゲノム変化と高次クロマチン動態との相互関係、さらにその後の細胞運命変化に与える影響はまだ明らかではありません。私はこれまで、ヒトiPS細胞を起点とした試験管内始原生殖細胞誘導系の確立と、細胞株による分化傾向性の違いを解析してきました。さらに、株間比較エピゲノム解析により多様性(不均一性)を示す領域を同定し、そのゲノム特性を解析してきました。本研究では、ヒトiPS細胞に潜在するエピゲノム多様性領域に着目し、クロマチン高次状態との連関機序の理解を目指します。さらに、試験管内始原生殖細胞誘導分化系を用いて、多能性細胞に潜在するエピゲノム多様性が、始原生殖細胞で誘発されるエピゲノムリプログラミング過程およびその後の生殖細胞分化に与える影響を理解することを目指します。これらの研究を通じて、エピゲノムリプログラミング現象に伴う非ゲノム情報の変換および維持を協調する分子制御メカニズムの理解、さらにはエピゲノムリプログラミング過程のロバストネスの理解を目指します。
主な論文
1) Nagano, M., Hu, B., Yokobayashi, S., et al., *Saitou, M. (30人中3番目) Nucleome programming for the foundation of totipotency in mammalian germline development. EMBO, in press.
2) *Yokobayashi, S., et al. (11人中1番目) Inherent genomic properties underlie the epigenomic heterogeneity of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Rep, 37(5), 109909 (2021).
3) Yamashiro, C., Yokobayashi, S., et al., *Saitou, M. (5人中3番目) Generation of human oogonia from induced pluripotent stem cells in culture. Nat Prot, 15, 1560-1583 (2020).
4) *Yokobayashi, S. and *Saitou, M. (2人中1番目) Reconstitution of germ cell development in vitro. Cell Biology of the Ovary, Springer, Singapore (2018).
5) *Yokobayashi, S., et al., *Saitou, M. (7人中1番目) Clonal variation of human induced pluripotent stem cells for induction into the germ cell fate. Biol Reprod, 96, 1154-1166 (2017).
